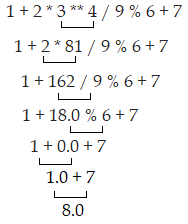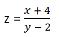Operators
Operators are special symbols which represents computation. They are applied on operand(s), which can be values or variables. Same operator can behave differently on different data types. Operators when applied on operands form an expression. Operators are categorized as Arithmetic, Assignment, Relational and Logical. Value and variables when used with operator are known as operands.
Arithmetic Operator
| Operator | Name | Example |
| + | Addition | x + y |
| - | Subtraction | x - y |
| * | Multiplication | x * y |
| / | Division | x / y |
| % | Modulus | x % y |
| ** | Exponentiation | x ** y |
| // | Floor division | x // y |
Example
>>> x = 10
>>> y = 3
>>> x + y
13
>>> x - y
7
>>> x * y
30
>>> x / y
3.3333333333333335
>>> x % y
1
>>> x ** y
1000
>>> x // y
3
Assignment Operators
| Operator | Example | Same As |
| = | x = 5 | x = 5 |
| += | x += 3 | x = x + 3 |
| -= | x -= 3 | x = x – 3 |
| *= | x *= 3 | x = x * 3 |
| /= | x /= 3 | x = x / 3 |
| %= | x %= 3 | x = x % 3 |
| //= | x //= 3 | x = x // 3 |
| **= | x **= 3 | x = x ** 3 |
Example:
>>> x = 5
>>> x
5
>>> x += 3
>>> x
8
>>> x -= 3
>>> x
5
>>> x *= 3
>>> x
15
>>> x /= 3
>>> x
5.0
>>> x %= 3
>>> x
2.0
>>> x **= 3
>>> x
8.0
>>> x //= 3
>>> x
2.0
Relational Operators
| Operator | Name | Example |
| == | Equal | x == y |
| != | Not equal | x != y |
| > | Greater than | x > y |
| < | Less than | x < y |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | x >= y |
| <= | Less than or equal to | x <= y |
Example
>>> x = 10
>>> y = 3
>>> x == y
False
>>> x != y
True
>>> x > y
True
>>> x < y
False
>>> x >= y
True
>>> x <= y
False
Logical Operator
| Operator | Description | Example |
| and | Returns True if both statements are true | x < 5 and x < 10 |
| or | Returns True if one of the statements is true | x < 5 or x < 4 |
| not | Reverse the result, returns False if the result is true | not(x < 5 and x < 10) |
>>> x = 6
>>> x < 5 and x < 10
False
>>> x < 5 or x < 10
True
>>> not(x < 5 and x < 10)
True
in Operator
In Python you can use the in operator to determine whether an item is contained in a sequence.
>>> number = 33
>>> number in (10,4,33,99)
TrueThe expression returns true if item is found in the sequence or false otherwise.
Operator Precedence
Precedence of operator - Listed from high precedence to low precedence.
| Operator | Description |
| ** | Exponentiation (raise to the power) |
| + , - | unary plus and minus |
| * , /, %, // | Multiply, divide, modulo and floor division |
| + , - | Addition and subtraction |
| <, <=, >, >= , ==, != | Comparison operators |
| not | Boolean NOT |
| And | Boolean AND |
| Or | Boolean OR |
Algebraic Expression to Python Statement
|
Algebraic Expression |
Python Statement |
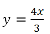
|
y = 4 * x / 3 |
|
z = 3xy + 7 |
z = 3 *x * y + 7 |
|
|
z = (x + 4) / (y - 2) |
Question: Evaluate the Following statement.
34 + 12 / 4 – 45
Solution:
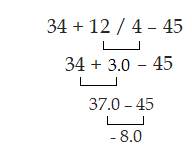
Question: Evaluate the Following statement
1 + 2 * 3 ** 4 / 9 % 6 + 7
Solution: